- Country: Regional
- Component: Water resources
News
- Country: Regional
- Component: Water resources
- Country: Regional
- Component: Water resources, Environmental Data
On 4 October, the EU4Environment-Water and Data programme lead a session on water-energy nexus challenges as part of the third edition of the Autumn Digital EU4Energy Week for Eastern Partnership Universities organised by the EU4Energy Programme Phase II.
The event aims to empower young people and provide them with the insights and contacts that will help them to shape the energy sector in their countries – Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, the Republic of Moldova, and Ukraine.
Participating students have the opportunities to meet with EU experts from various organisations in the energy sector, such as the Council of European Energy Regulators, the International Energy Agency, the Energy Community Secretariat, and from experts from the UNECE and International Office for Water (implementing partners of the EU4Environment Water and Data programme).
The 2023 edition of the Autumn Digital EU4Energy Week for EaP Universities focuses on the implementation of the Clean Energy Package and the EU Green Deal, the role of hydrogen in the energy transition, energy poverty, and technological solutions for the energy transition.
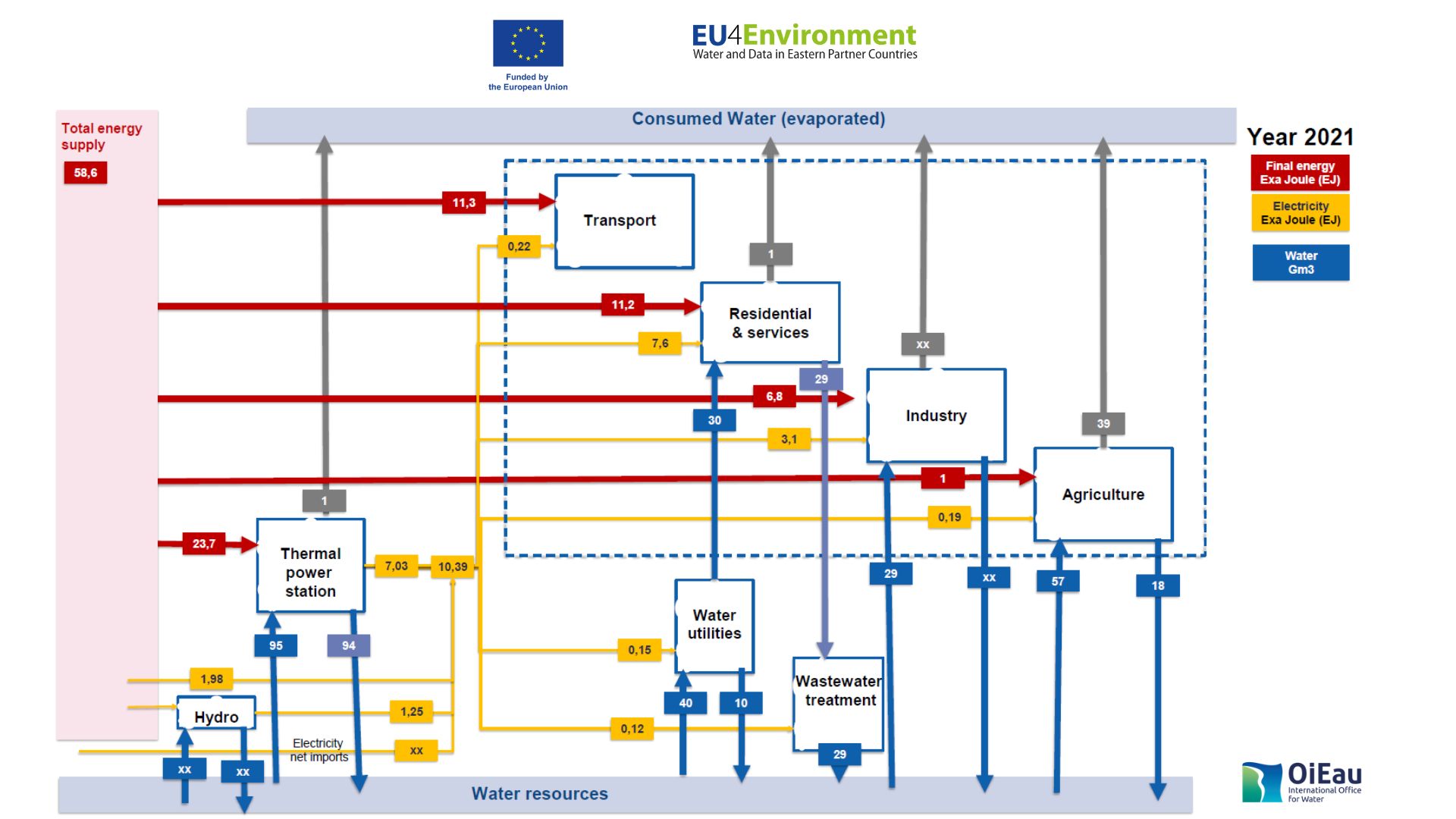
The lecture of the EU4Environment Water and Data programme described a matrix representing the major water and energy flows needed for human activities and the issues involved. The focus is made on energy requirements for water use and on water requirements for energy production. The objectives were to identify and define the basic vocabulary for studying water and energy flows, to give quantified orders of magnitude and to identify the strong links that exist between the use of water and energy.
As part of the event, participating students will take a quiz on the topics covered. The highest scoring student will attend a conference and meet energy professionals working in the sector.
Presentation on water-energy nexus:
- Introduction (UNECE)
- Water-Energy nexus (OiEau)
Webpage of the event: https://www.eap-events.eu/ehome/index.php?eventid=200267446&
Recording of all sessions and access to all presentations: https://euneighbourseast.eu/news/latest-news/autumn-digital-eu4energy-week-for-eastern-partnership-universities-launched-in-brussels/
- Country: Regional
- Component: Water resources
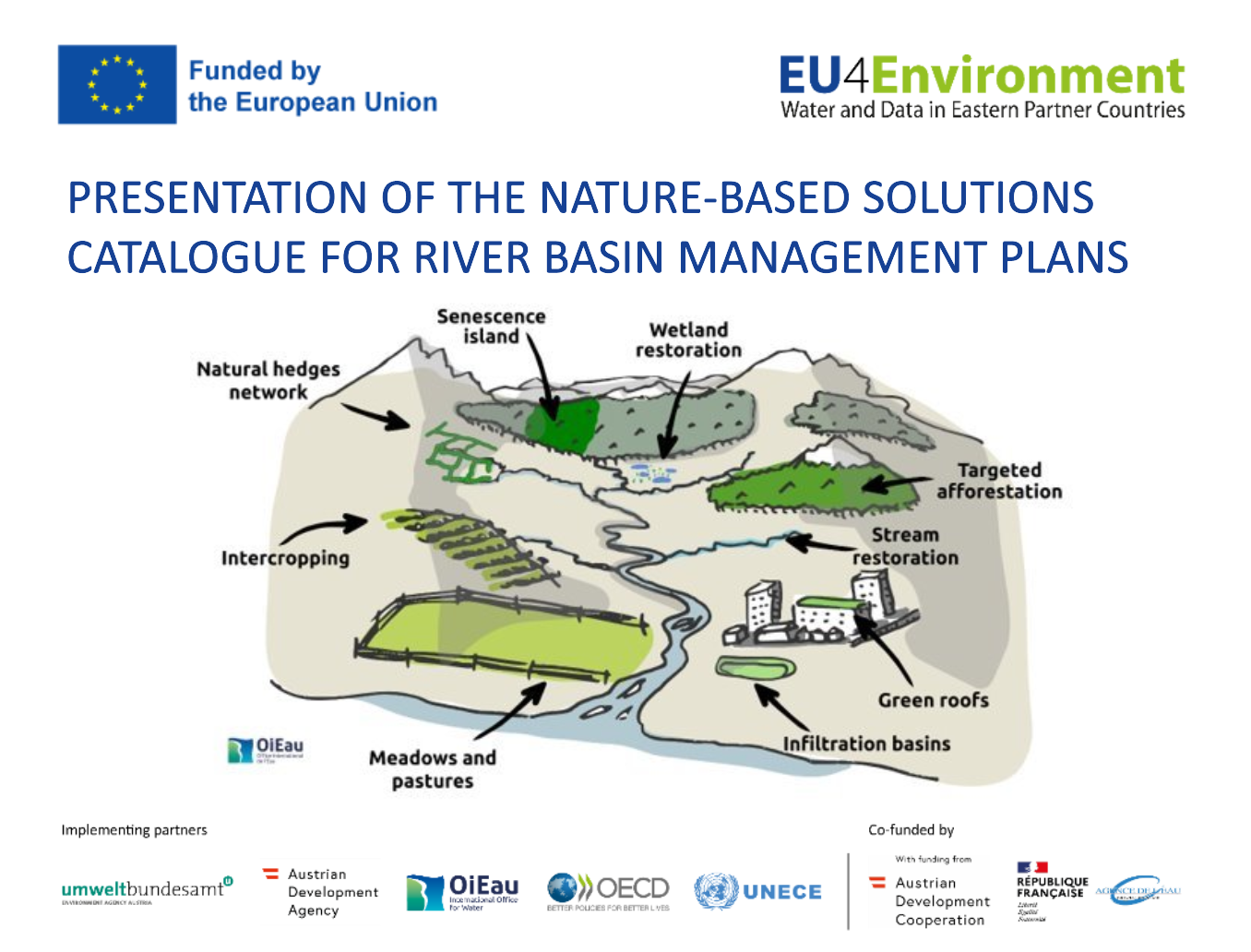
On July 6th, 2023, the EU4Environment Water and Data programme organised an online regional workshop focusing on nature-based solutions in Eastern Partner countries. The workshop gathered over 100 participants, including experts from Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Moldova, and Ukraine. Their shared experiences centered around the implementation of nature-based solutions to combat soil erosion, mitigate floods, and address biodiversity loss.
The workshop's primary objective is to foster a deeper understanding and acceptance of nature-based solutions among Eastern Partner countries. This understanding is essential for integrating nature-based solutions into the programmes of measures of River Basin Management Plans. Currently, such plans are being developed in Armenia (Northern river basin), Georgia (Enguri and Rioni river basins), and Ukraine (Dnipro river basin). Nature-based solutions are seen as relevant measures within these plans because they address societal challenges while simultaneously preserving biodiversity and natural resources.
The insights shared during the workshop will play a valuable role in the development of a comprehensive catalogue on nature-based solutions. This catalogue is being developed by the International Office for Water as part of the programme. Its aim is to facilitate the incorporation of practical and effective nature-based solutions into the river basin management plans of Eastern Partner countries.
The importance of nature-based solutions lies in their cost-effectiveness and sustainability, particularly when driven by local leadership. Implementing successful nature-based solutions requires understanding the local context and involving various partners who may not typically collaborate. Additionally, traditional cost-benefit analyses need to be adapted to fully capture the positive impacts of nature-based solutions on the environment, but also contribute to reducing the effects of climate change while promoting social and economic development in the countries.
Finally, the participants stressed the significance of preserving existing natural ecosystems as the best form of nature-based solutions. By protecting and conserving these ecosystems, it becomes possible to enhance their natural functions and benefits.
Presentations and useful resources
- Armenia – Rehabilitation of Khor Virap Ramsar site (PDF)
- Azerbaijan – Kura Delta ecological restoration (PDF)
- Georgia – Flourishing dams against suspended matter pollution (PDF)
- Video about the Sustainable Caucasus project (in Georgian)
- Handbook on integrated erosion control, a practical guide for planning and implementing integrated erosion control measures in Georgia, GIZ (IEC IBIS projects, 2019 - 2020)
- Moldova – Constructed wetlands for sanitation (PDF)
- Ukraine – Contour and melioration agriculture (PDF)
- European Commission, DG ENV – Trends in Nature-based Solutions (PDF)
- Publication “Evaluating the impact of nature-based solutions” A handbook for practitioners / A summary for policy makers
- UNECE – Nature-based Solutions for water resources (PDF)
- OECD – On-going work supporting the financing of Nature-based Solutions in the EaP countries (PDF)
- OiEau – Presentation of the Nature-based Solutions catalogue (PDF)
- OiEau - Nature-based Solution as measures of River Basin Management Plans (PDF)
- Country: Regional
- Component: Environmental Data
More than 100 participants took part to the regional webinar co-organised by the Covenant of Mayors East and the EU4Environment Water and Data programme. The aim was to raise awareness of municipalities about the impact of air pollution, and to showcase good practice examples to reduce Particulate Matters emissions from major sources.
National workshops building on this regional webinar will follow in Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, Moldova and Ukraine at the end of September.
Air pollution is the main environmental threat to human health. The World Health Organization (WHO) assumes that around 7 million premature deaths are globally related to air pollution. The pollutant with the most severe health impacts is fine particulate matter, PM2.5.
The main sources of PM2.5 are domestic heating with biomass or coal, diesel vehicles, open burning of waste and agricultural waste, industry and power plants. A number of good practice examples are available that can be implemented to reduce emissions of PM2.5 from these sources. In most cases, these measures contribute to further environmental topics such as climate change and noise as well as improving energy security and mobility.
Presentations:
- Municipalities act for climate and sustainable energy use (including “My Air Quality” tool by JRC)
- Health impacts and main sources of PM
- Possible mitigation measures for domestic heating, agricultural waste burning, electricity generators, traffic
- Energy poverty
- There’s something in the air – Communicating Air Quality and mitigation measures
- Country: Regional
- Component: Water resources, Environmental Data
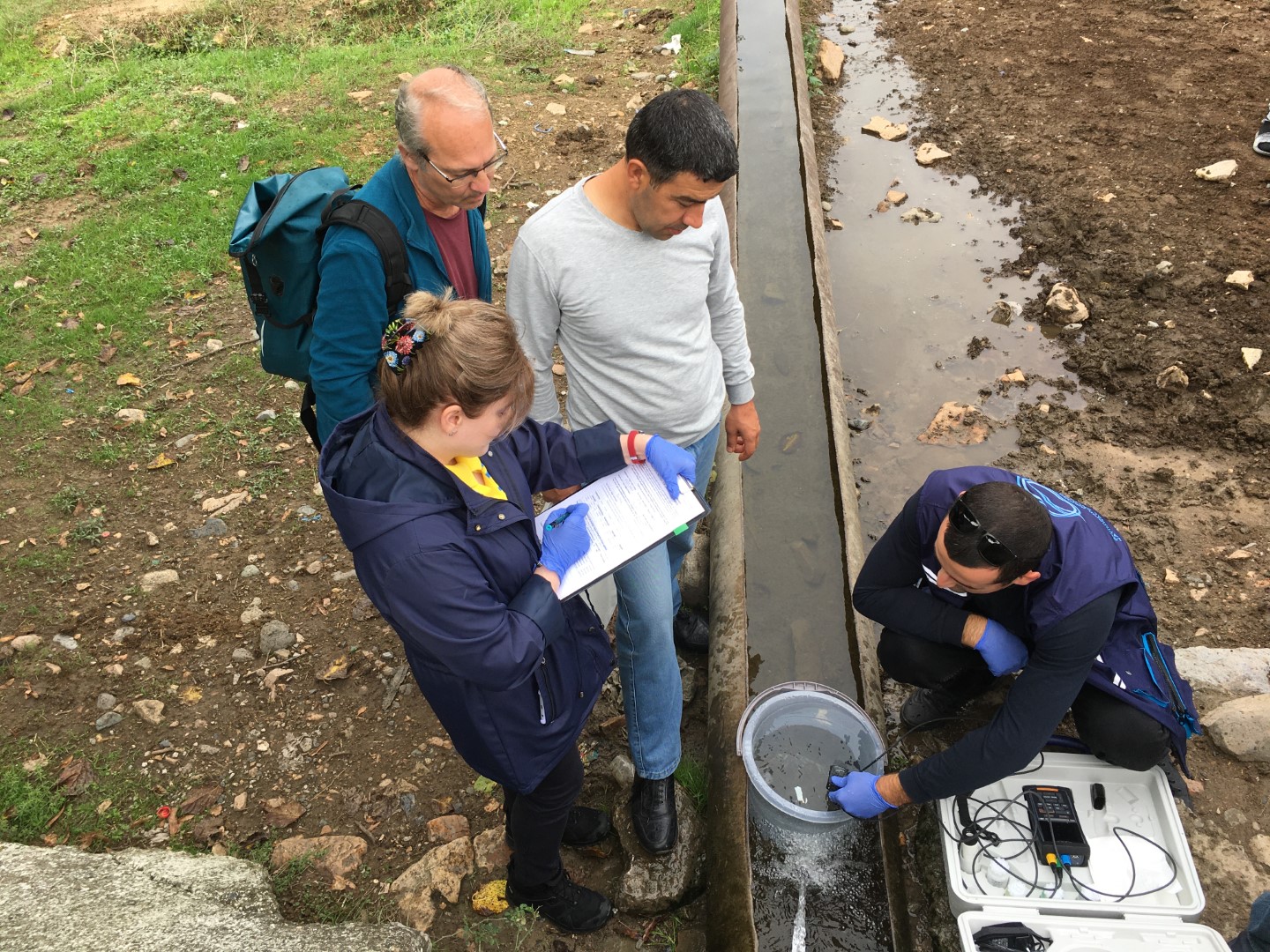
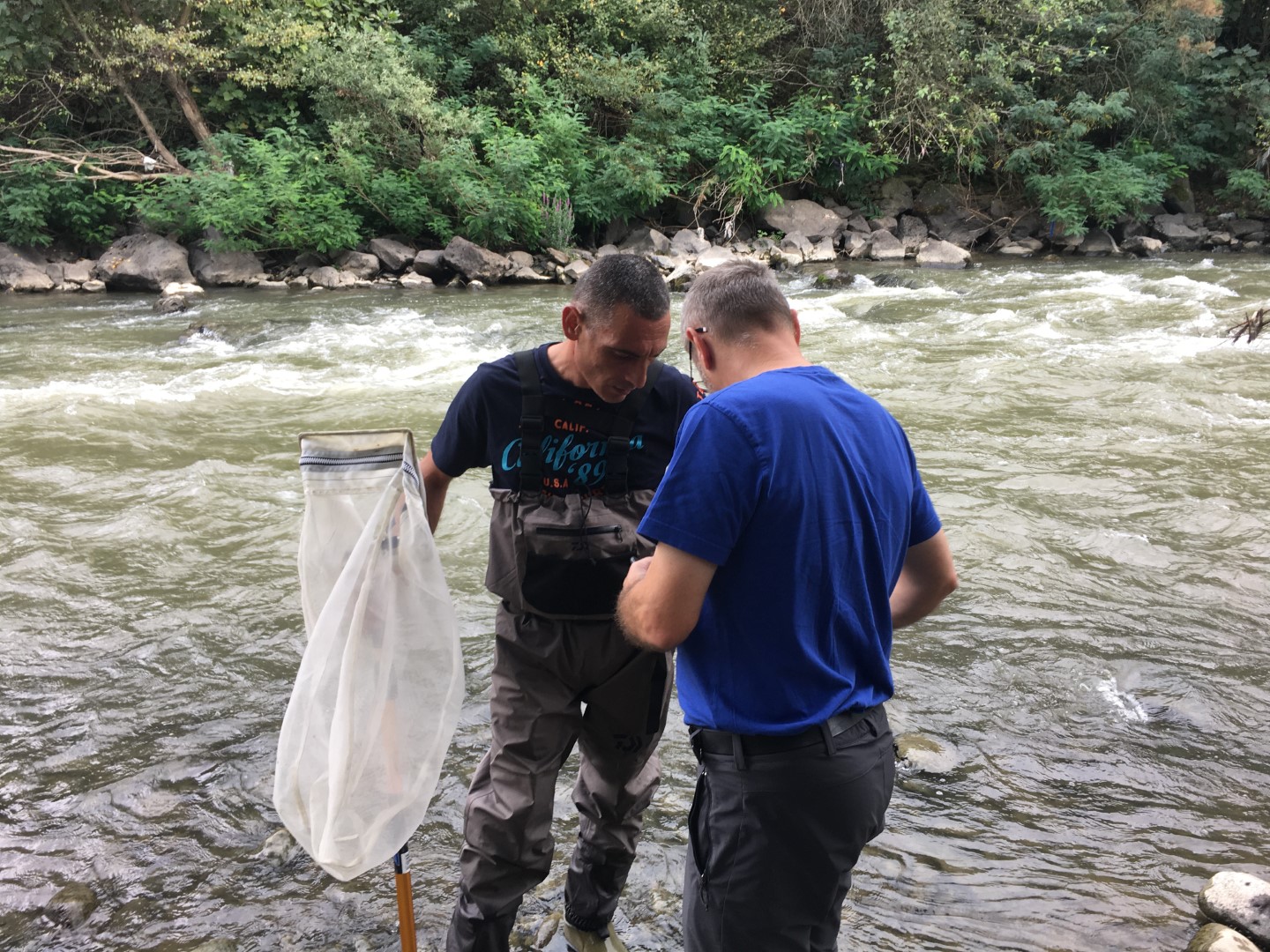
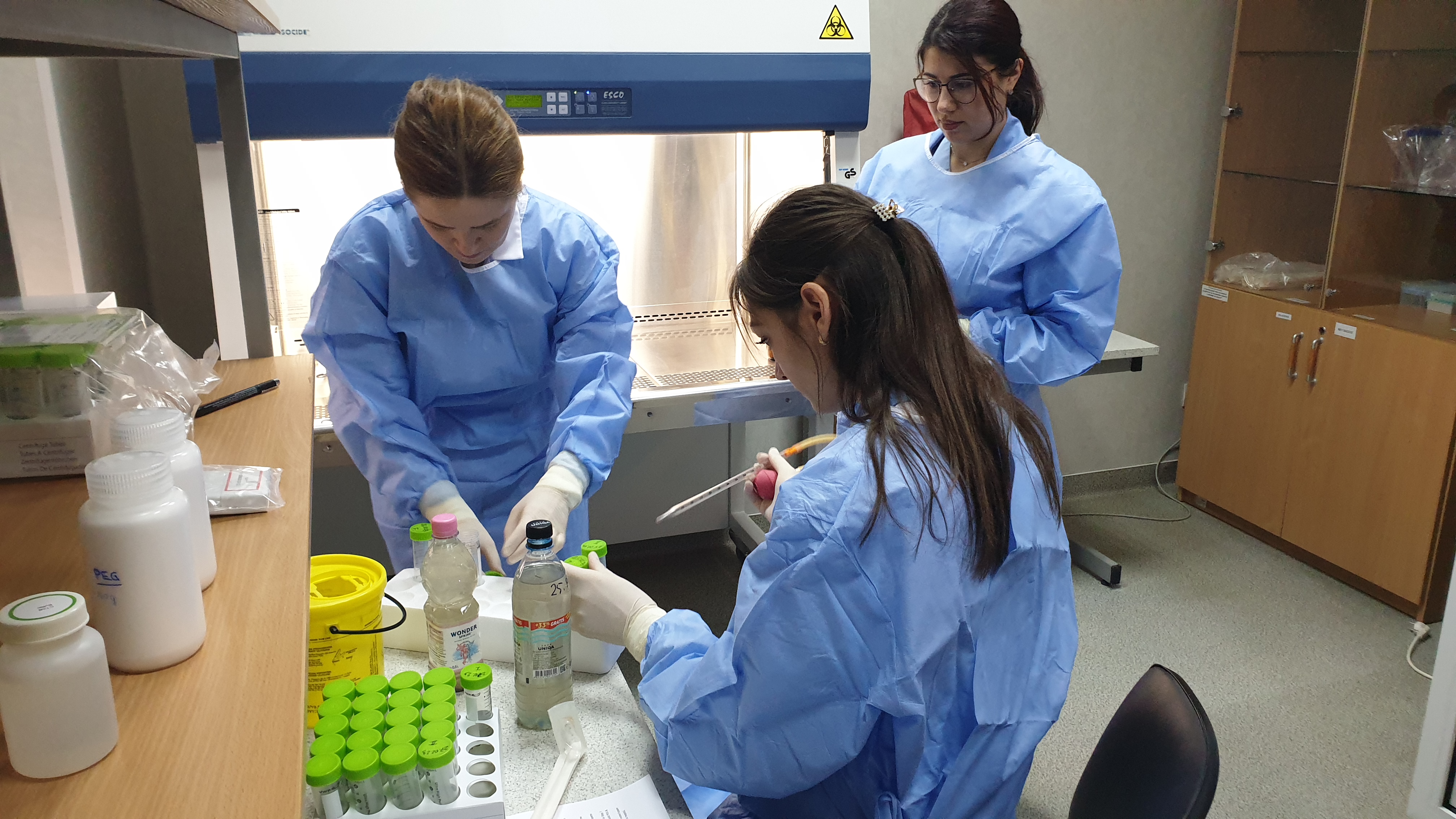
Wastewater is a mirror of our civilization and an effective early warning system for the spreading of contagious diseases. Through the EU4Environment Water and Data program, the European Union supports its Eastern Partner countries in the further development of wastewater monitoring and in institutionalizing this new powerful tool for public health protection.
On 3 July 2023, upfront the WHO Ministerial Conference on Environment and Health in Budapest, a high-level workshop brings together ministers and other decision-makers of the Eastern Partner countries with EU representatives to address the need for a national wastewater-based epidemiology policy and regulation in the region. Aim of the workshop is to review the power and benefits of this tool and to initiate the relevant policy processes in the partner countries to formally establish a surveillance that can easily coordinate with the EU and other global actors. Austrian experts will highlight progress and further needs at the workshop and in a side event at the WHO Ministerial Conference on July 5.
“Together, the European Union and our Eastern partners were able to overcome enormous challenges posed by the pandemic”, explains Lawrence Meredith, director of the EU Directorate-General for Neighbourhood and Enlargement Negotiations. “The next step will be to set up routine wastewater epidemiological testing as soon as possible. The European Union is ready to make this next step together with the Eastern Partner countries.”
“In order to ensure establishment, sustainability and reliability of national wastewater-based epidemiology programmes, it is essential to define procedures with allocated responsibilities at the health and environment sectors. Countries need to arrange formal commitment from relevant national actors and ensure adequate resourcing. Our program has laid the foundation for this”, states Alexander Zinke, project leader of EU4Environment Water and Data.
“We are keen to share the EU experience and strengthen regular coordination with key actors at EU and the global level” says Bernd Gawlik from the EU Joint Research Centre, stressing the global dimension of wastewater-based epidemiology.
Wastewater-based epidemiology has been established since 2021 throughout Europe as a cost-effective, rapid and reliable source of epidemiologic information for national health authorities, local health care and national disease control centers, public and private wastewater operators, and water and environment agencies. Triggered by the Covid-19 pandemic, wastewater surveillance of the spread of infections is becoming a global standard that has clear advantages compared for instance to clinical testings. The EU4Environment Water and Data program initiated in April 2022 the introduction of wastewater-based epidemiology to Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia and Republic of Moldova, supports Ukraine and keeps on transferring the EU and Austrian experience and know how on this topic in close coordination with the European Commission.